Scale-adaptive Auto-context-guided Fetal US Segmentation with Structured Random Forests
Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal, https://doi.org/10.15212/bioi-2020-0016. In this article the authors Xin Yang, Haoming Li, Li Liu, and Dong Ni from Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China and Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China consider Scale-adaptive Auto-context-guided Fetal US Segmentation with Structured Random Forests.
Accurate measurement of fetal biometrics in ultrasound at different trimesters is essential in assisting clinicians to conduct pregnancy diagnosis. However, the accuracy of manual segmentation for measurement is highly user dependent.
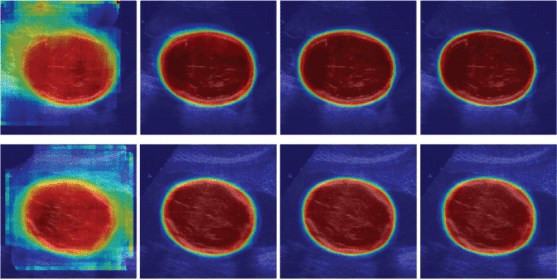
The authors of this article design a general framework for automatically segmenting fetal anatomical structures in two-dimensional (2D) ultrasound (US) images thus making objective biometric measurements available. Structured random forests (SRFs) are introduced as the core discriminative predictor to recognize the region of fetal anatomical structures with a primary classification map. The patch-wise joint labeling presented by SRFs has inherent advantages in identifying an ambiguous/fuzzy boundary and reconstructing incomplete anatomical boundary in US.
To obtain a more accurate and smooth classification map, a scale-adaptive auto-context model is then injected to enhance the contour details of the classification map from various visual levels. Final segmentation can be obtained from the converged classification map with thresholding. The framework is validated on two important biometric measurements: fetal head circumference (HC) and abdominal circumference (AC).
The final results illustrate that the authors proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of segmentation accuracy.
Article reference: Xin Yang, Haoming Li, Li Liu, and Dong Ni, Scale-adaptive Auto-context-guided Fetal US Segmentation with Structured Random Forests. BIO Integration, 2020, https://doi.org/10.15212/bioi-2020-0016.
BIO Integration is fully open access journal which will allow for the rapid dissemination of multidisciplinary views driving the progress of modern medicine.
As part of its mandate to help bring interesting work and knowledge from around the world to a wider audience, BIOI will actively support authors through open access publishing and through waiving author fees in its first years. Also, publication support for authors whose first language is not English will be offered in areas such as manuscript development, English language editing and artwork assistance.
BIOI is now open for submissions; articles can be submitted online at:
https://mc04.manuscriptcentral.com/bioi
Please visit www.bio-integration.org to learn more about the journal.
Editorial Board: https://bio-integration.org/editorial-board/
BIOI is available on the IngentaConnect platform (https://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cscript/bioi) and at the BIO Integration website (www.bio-integration.org).
Submissions may be made using ScholarOne (https://mc04.manuscriptcentral.com/bioi).
There are no author submission or article processing fees.
Follow BIOI on Twitter @JournalBio; Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/BIO-Integration-Journal-108140854107716/) and LinkedIn (https://www.linkedin.com/company/bio-integration-journal/).
ISSN 2712-0074
eISSN 2712-0082
Keywords: ultrasound image segmentation, contour enhancement, structured random forests, fetal biometrics, automatic measurement