Health benefits of liquid smoke from various biomass sources: a systematic review
Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. Liquid smoke, a product of the pyrolysis process, includes components such as phenol, furfural, and ketones, and has acidic characteristics. Liquid smoke from various biomass sources has been used as a natural preservative worldwide and reported to be safe in humans. As a bio-economic product, liquid smoke has human health benefits.
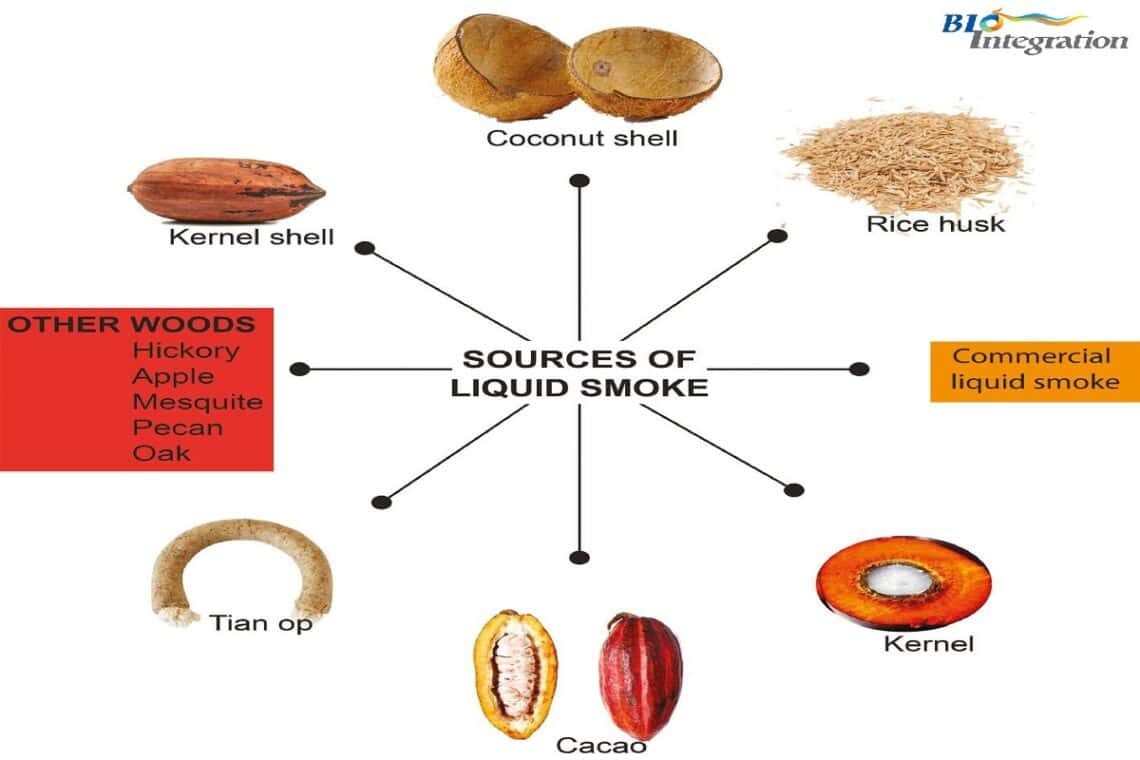
This article analyzes and describes the health benefits of liquid smoke from various biomass sources, according to in silico, in vitro, and in vivo studies. A systematic review following PRISMA guidelines was conducted to identify published reports of liquid smoke from various biomass sources. The anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, anti-diabetic, wound healing, and anti-periodontitis activity of liquid smoke was analyzed. Prior research has investigated liquid smoke produced through pyrolysis of various biomass types, such as rice husks (Oryza sativa), coconut shells (Cocos nucifera L.), palm kernels ( Elaeis guineensis Jacq.), cocoa pods ( Theobroma cacao L .), tian op, and hickory ( Carya tomentosa (Lam.) Nutt .), as well as commercial liquid smoke. Toxicity testing, and in vitro and in vivo studies, are required for the assessment of health benefits.
Therapeutic benefits of liquid smoke including anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive, anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, and anti-viral activity have been described. Further health benefits include anti-diabetic, anti-periodontitis, wound healing, and ulcer healing activity. These findings increase the use value of liquid smoke as a natural product with human health benefits.
Read More: https://www.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.15212/bioi-2024-0083
BIO Integration is fully open access journal which will allow for the rapid dissemination of multidisciplinary views driving the progress of modern medicine. As part of its mandate to help bring interesting work and knowledge from around the world to a wider audience, BIOI will actively support authors through open access publishing and through waiving author fees in its first years. Also, publication support for authors whose first language is not English will be offered in areas such as manuscript development, English language editing and artwork assistance.
BIOI is now open for submissions; articles can be submitted online at: https://mc04.manuscriptcentral.com/bioi
There are no author submission or article processing fees.
Please visit www.bio-integration.org to learn more about the journal.
Editorial Board: https://bio-integration.org/editorial-board/
BIOI is available on the ScienceOpen platform.
Follow BIOI on Twitter @JournalBio; Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/BIO-Integration-Journal-108140854107716/) and LinkedIn (https://www.linkedin.com/company/bio-integration-journal/).
ISSN 2712-0074
eISSN 2712-0082
Meircurius Dwi Condro Surboyo, Saeid Baroutian and Widyah Puspitasari et al. Health benefits of liquid smoke from various biomass sources: a systematic review. BIOI. 2024. Vol. 5(1). DOI: 10.15212/bioi-2024-0083